# 时间复杂度
1、如果算法的执行时间不随着问题n的增加而增加,执行的时间仍然是个常数,此类算法的时间复杂度为O(n)
let x = 1;
while(x<10) {
x++;
}
1
2
3
4
2
3
4
2、如果有若干个循环的话,算法的时间复杂度随着嵌套的层数决定。外层每循环1次内层就循环n次。时间复杂的O(n^2)
for(let i=0;i<n;i++>) {
for(let j=0;j<n;j++>) {
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
2
3
4
5
循环不止与n有关,还与执行所满足的判断条件有关
domdiff的时间复杂度是O(n)
# domdiff
1、虚拟dom 能够最小化的操作dom,集合一些优化dom的属性优化,数据动态的给你觉得信任的组件,封装组件 2、Dom diff 区分到哪还在这颗树上,哪里发生了变化 3、patch 打补丁 4、div>p
# Virtual-dom
Virtual-dom是一系列的模块集合,用来提供声明式的DOM渲染。来看一个简单的DOM片段,本质上就是在js和dom之间做了个缓存。可以类比CPU和硬盘,既然硬盘这么慢我们就在JS和DOM之间加个缓存。CPU(js)只操作内存(Virtual-dom),最后的时候再把变更写进硬盘(DOM)
const dom = {
tagName:'div',
props:{
id:'parent'
},
children:[
{tagName:'span',props:{class:'child'},children:['item1']},
{tagName:'span',props:{class:'child'},children:['item2']},
{tagName:'span',props:{class:'child'},children:['item3']},
]
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
代码实现一下Virtual-dom
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="module" src="js/index.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
index.js
import { createElement } from './element.js'
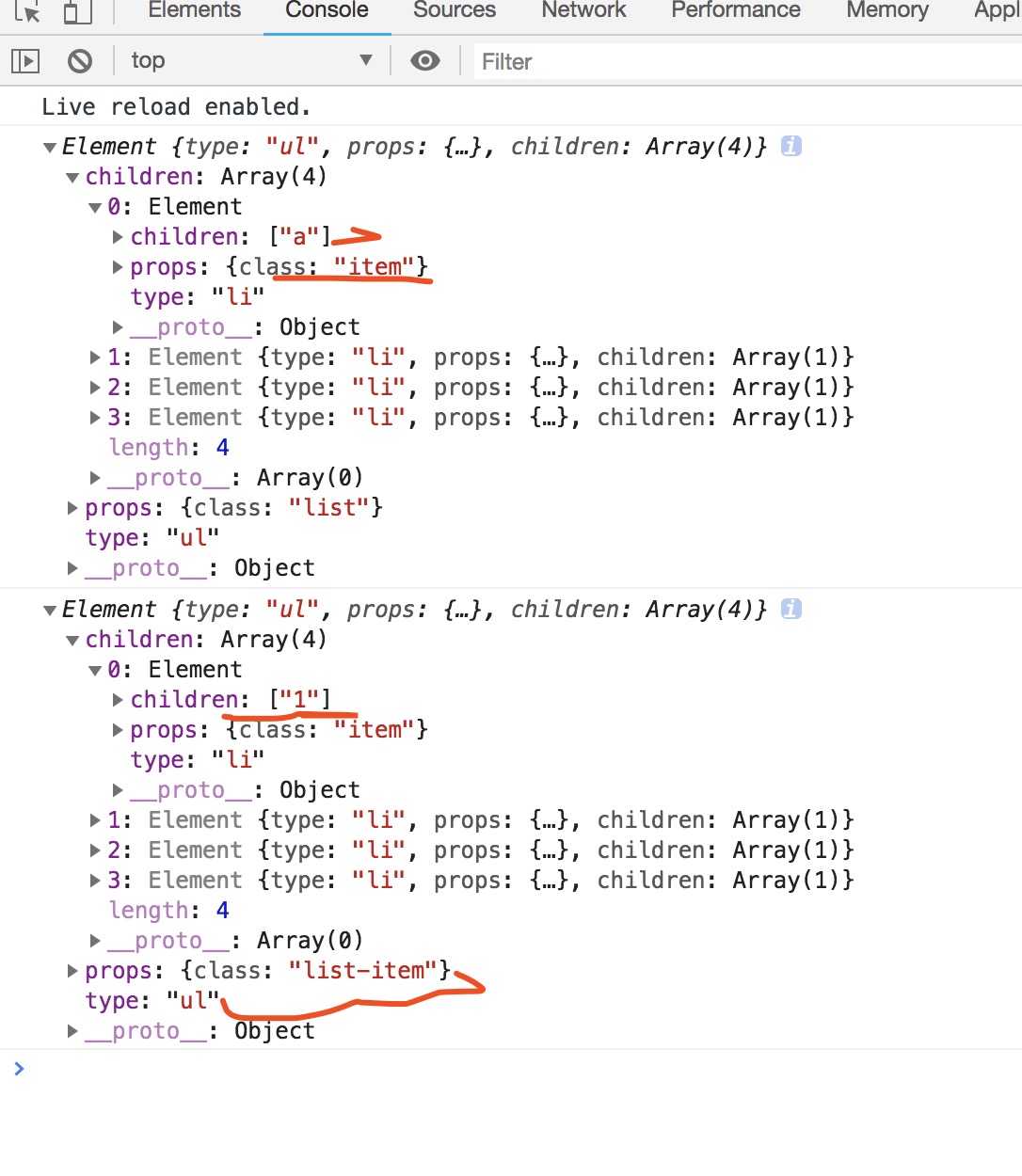
let VirtualDom1 = createElement('ul', { class: 'list' }, [
createElement('li', { class: 'item' }, ['a']),
createElement('li', { class: 'item' }, ['b']),
createElement('li', { class: 'item' }, ['c']),
createElement('li', { class: 'item' }, ['d']),
])
let VirtualDom2 = createElement('ul', { class: 'list-item' }, [
createElement('li', { class: 'item' }, ['1']),
createElement('li', { class: 'item' }, ['b']),
createElement('li', { class: 'item' }, ['c']),
createElement('li', { class: 'item' }, ['4']),
])
console.log(VirtualDom1)
console.log(VirtualDom2)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
element.js
class Element {
constructor(type, props, children) {
this.type = type;
this.props = props;
this.children = children;
}
}
function createElement(type, props, children) {
return new Element(type, props, children)
}
export {
createElement
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
# 代码实现domDiff (不存在key的情况下)
# 目前我们存在的情况 2号位置 a变成1 8号位置d变成4
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
</div>
<script type="module" src="js/index.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
index.js
import { createElement } from './element.js'
import { diff } from './dom-diff.js'
let VirtualDom1 = createElement('ul', { class: 'list' }, [
createElement('li', { class: 'item' }, ['a']),
createElement('li', { class: 'item' }, ['b']),
createElement('li', { class: 'item' }, ['c']),
createElement('li', { class: 'item' }, ['d']),
])
let VirtualDom2 = createElement('ul', { class: 'list-item' }, [
createElement('li', { class: 'item' }, ['1']),
createElement('li', { class: 'item' }, ['b']),
createElement('li', { class: 'item' }, ['c']),
createElement('li', { class: 'item' }, ['4']),
])
console.log(VirtualDom1)
console.log(VirtualDom2)
//将虚拟DOM 渲染到页面 $dom=>VirtualDom1=>oldTree
// let $dom = render(VirtualDom1)
// renderDom($dom,document.getElementById('app'))
//======假设用户这个时候调用了SetState========
//得到补丁包
const patchs = diff(VirtualDom1, VirtualDom2)
console.log(patchs,'21212')
//将布丁包直接更新到DOM
// Patchs($dom,$patchs)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
dom-diff.js
//1.{type:"ATTRS",attrs:{class:"list-item"}}
//2.{type:"REMOVE",index:3}
//3.{type:"TEXT",text:1}
//4.{type:"REPLACE",newNode:newNode}
//补丁包
// {
// 0:{type:"ATTRS",attrs:{class:"list-item"}},
// 2.{type:"TEXT",text:1},
// 8.{type:"TEXT",text:4}
// }
/**
* 生成的补丁包 样式上面一样
*/
import _ from "./util.js";
let patchs = {};
//全局索引
let globalIndex = 0;
function diff(oldTree, newTree) {
dfswalk(oldTree, newTree, globalIndex);
return patchs;
}
function dfswalk(oldTree, newTree, index) {
//每个元素都有一补丁对象
let currentPatchs = [];
//如果新节点不存在
if (!newTree) {
currentPatchs.push({
type: "REMOVE",
index
})
} else if (_.isString(oldTree)) {
if (_.isString(newTree) && oldTree != newTree) {
currentPatchs.push({
type: "REPLACE",
newNode: newTree
})
}
} else if (oldTree.type == newTree.type) {
//两个节点的元素类型一致
//比属性
//比子节点
diffChildrens(oldTree.children, newTree.children);
}
if (currentPatchs.length > 0) {
patchs[index] = currentPatchs;
}
}
function diffProps() {}
function diffChildrens(oldChildrens, newChildrens) {
oldChildrens.forEach((child, idx) => {
dfswalk(child, newChildrens[idx], ++globalIndex);
});
}
export {
diff
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
element.js
class Element {
constructor(type, props, children) {
this.type = type;
this.props = props;
this.children = children;
}
}
function createElement(type, props, children) {
return new Element(type, props, children)
}
export {
createElement
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
until.js
function util() {
}
util.isString = function (node) {
return typeof node === 'string';
}
export default util
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
这个地方如果跑我的代码 需要启一个服务 live-server webpack什么的
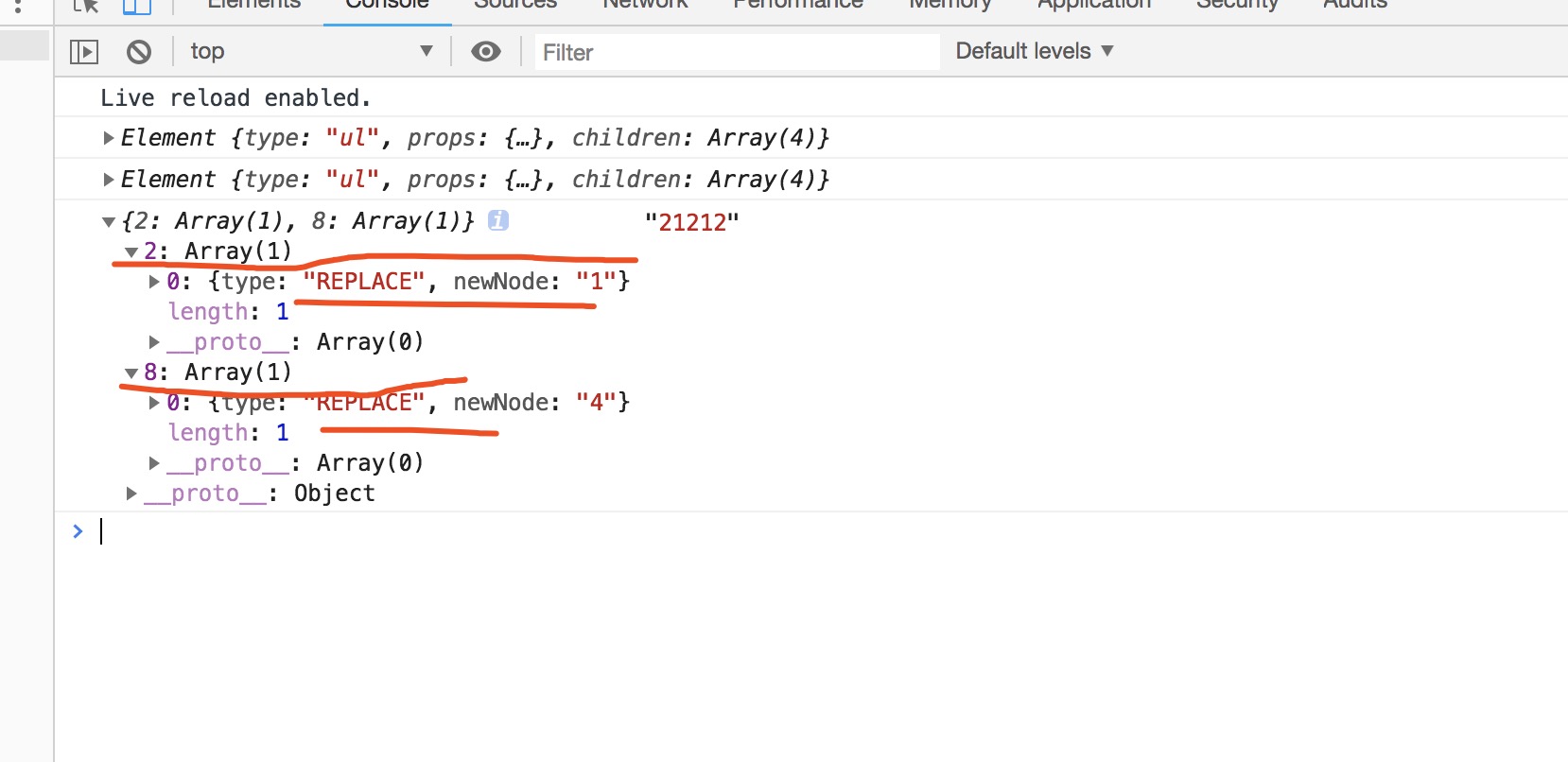
这里就简单的实现了一个基本的domdiff
← 数据结构 前端中的数据结构与算法(一) →