# webpackDemo
新建webpackDemo文件--->init--->install webpack---->install webpack-cli--->mkdir src touch index.js---->mkdir loader---->mkdir markdowm-loader.js
# loader
# 分析一下markdown-loader
https://github.com/peerigon/markdown-loader/blob/master/index.js
"use strict";
//分析mark源码工具
const marked = require("marked");
//webpack提供的工具集 收集用户options等 也就是webpack.**.js里module.export的配置等
const loaderUtils = require("loader-utils");
//提供一个对外的函数
module.exports = function (markdown) {
// merge params and default config
const options = loaderUtils.getOptions(this);
// 当前loader开启缓存
this.cacheable();
// 用户option--->mark
marked.setOptions(options);
//string
return marked(markdown);
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
webpack 为什么慢 机制分析 loader1 string(源代码)--->ast(eg1 遍历这颗🌲替换const->var)--->string loader2 接受loader2的string/buffer--->ast--->string
总结 出来loader不敢活,核心模块才干活 eg: a-loader 干活的是a
# 实现一个loader
loader/index.html
const loaderUtils = require("loader-utils");
//this 代表当前loader类
module.exports=function(content,map,meta) {
console.log('前置沟盖---->',this.data.value)
//拿到options
const options = loaderUtils.getOptions(this);
//为了避免使用正则过于复杂 ---->ast🌲
//content.replace('const','var')
return content+'console.log(1)';
}
module.exports.pitch = function(r,p,data) {
data.value = '🐶🐶🐶前置钩子'
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
webpack.config.js
const path = require('path');
module.exports = {
module:{
rules: [{
test: /\.js$/,
use: [
{
loader: path.resolve('./loader/index.js'),
options: {
data:"🍌🍌🍌:自定义loader"
}
}
]
}]
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
# Ast处理
Ast重要性
- postcss cssnext -> css
- webpack loader es6 -> ast -> es5
- vue template -> html ast -> vdom
- 8 写的js代码 词法分析 语法分析 ast->执行
- ast + 设计模式 发布订阅
//webpack使用生成ast的包
const acorn = require('acorn');
//webpack使用生成ast遍历工具
const walk = require('acorn-walk');
const MagicString = require('magic-string');
const source = 'const a = 100'
const result = acorn.parse(source);
const code = new MagicString(source);
console.log(result);
walk.simple(result, {
Literal(node) {
console.log(`Found a literal: ${node.value}`)
},
VariableDeclaration(node) {
console.log('🍌', node);
const { start } = node;
console.log('🍎', start);
code.overwrite(start, start + 5, "var")
}
})
console.log('结果🐟',code.toString())
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
# plugin
如何编写自己的插件 webpack实现插件机制的⼤大体⽅方式是: 「创建」—— webpack在其内部对象上创建各种钩⼦子; 「注册」—— 插件将⾃自⼰己的⽅方法注册到对应钩⼦子上,交给webpack; 「调⽤用」—— webpack编译过程中,会适时地触发相应钩⼦子,因此也 就触发了了插件的⽅方法。


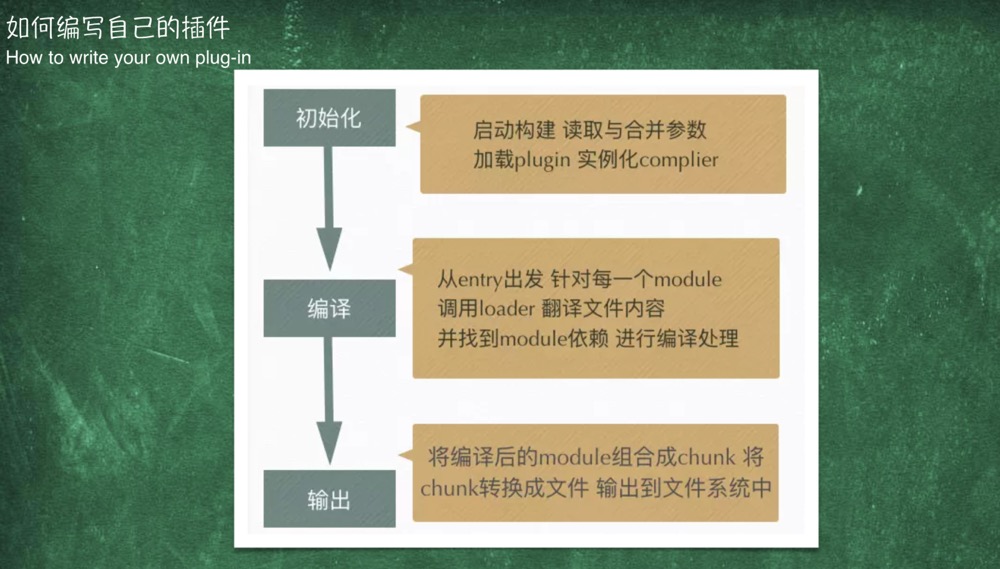

# 实现一个plugin
plugin/ConsoleLogOnBuildWebpackPlugin.js
class ConsoleLogOnBuildWebpackPlugin {
apply(compiler) {
compiler.hooks.run.tap(pluginName, compilation => {
console.log("webpack 构建过程开始!");
});
}
}
module.exports = ConsoleLogOnBuildWebpackPlugin;
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
webpack.config.js
const ConsoleLogOnBuildWebpackPlugin = require('./plugin/ConsoleLogOnBuildWebpackPlugin')
plugins:[
new ConsoleLogOnBuildWebpackPlugin()
]
2
3
4
运行代码npm run dev
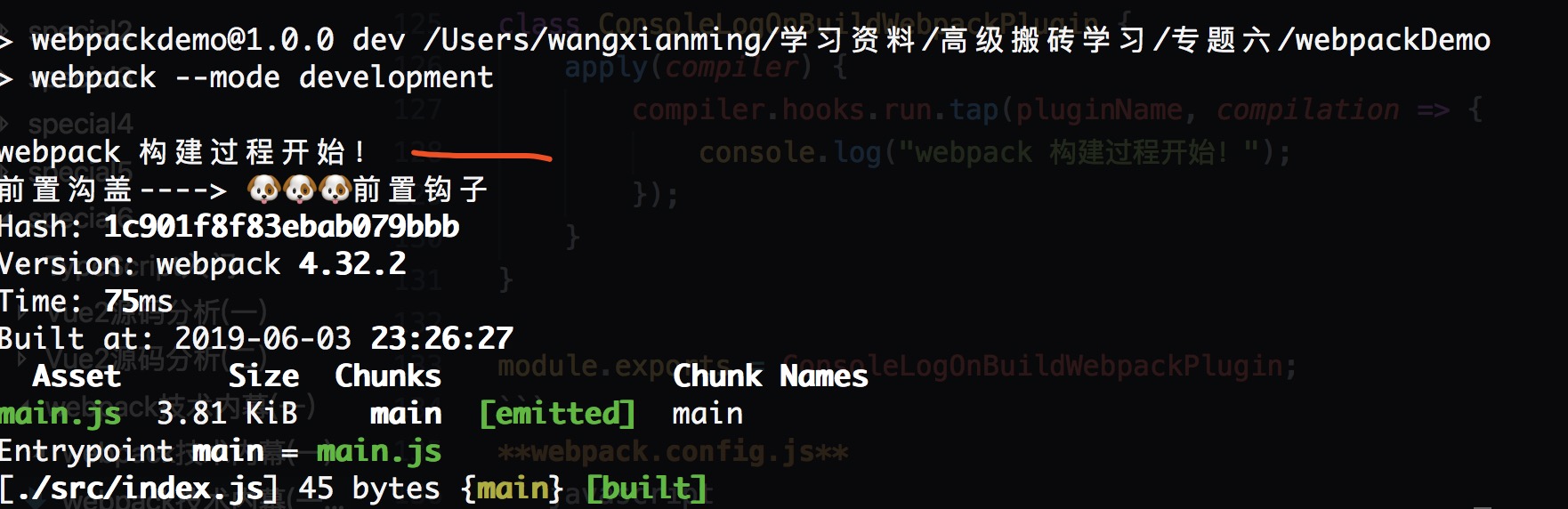
会发现虽然执行了,但是是最先执行的,带着这个疑问我们去看源码从webpack源码去寻找问题 webpack package.json "main": "bin/webpack.js", "main": "lib/webpack.js",
bin/webpack.js 可以看到webpack启动的需要依赖的原理 eg webpack-cli lib/webpack.js 发现了compiler
const Compiler = require("./Compiler");
compiler = new Compiler(options.context);
compiler.options = options;
new NodeEnvironmentPlugin().apply(compiler);
if (options.plugins && Array.isArray(options.plugins)) {
for (const plugin of options.plugins) {
if (typeof plugin === "function") {
plugin.call(compiler, compiler);
} else {
//调度所有的插件
plugin.apply(compiler);
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
./Compiler 发现了Compiler、AsyncSeriesHook 继承了tapable compiler.hooks.run.tap(pluginName, compilation) tap???compilation???tapable
const {
Tapable,
SyncHook,
SyncBailHook,
AsyncParallelHook,
AsyncSeriesHook
} = require("tapable");
class Compiler extends Tapable {
constructor(context) {
super();
this.hooks = {
run: new AsyncSeriesHook(["compiler"]),
};
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
tapable 发布订阅的模式 npm install --save tapable
plugin/demo1.js
const {
SyncHook,//同步串行钩子 不关系函数的返回值
SyncBailHook,
SyncWaterfallHook,
SyncLoopHook,
AsyncParallelHook,
AsyncParallelBailHook,
AsyncSeriesHook,
AsyncSeriesBailHook,
AsyncSeriesWaterfallHook
} = require("tapable");
let queue = new SyncHook(['name1','name2']);
//订阅
queue.tap('1',function(name1,name2) {
console.log('1⃣️',name1,name2);//'小明','小红'
})
queue.tap('2',function(name1,name2) {
console.log('2⃣️',name1,name2);//'小明','小红'
})
//发布
queue.call('小明','小红')
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
compilation compilation与compiler执行同理 存放着所有执行的chunk npm install html-webpack-plugin --save-dev
html-webpack-plugin
compiler.hooks.compilation.tap('HtmlWebpackPluginHooks', compilation => {
const SyncWaterfallHook = require('tapable').SyncWaterfallHook;
const AsyncSeriesWaterfallHook = require('tapable').AsyncSeriesWaterfallHook;
compilation.hooks.htmlWebpackPluginAlterChunks = new SyncWaterfallHook(['chunks', 'objectWithPluginRef']);
compilation.hooks.htmlWebpackPluginBeforeHtmlGeneration = new AsyncSeriesWaterfallHook(['pluginArgs']);
compilation.hooks.htmlWebpackPluginBeforeHtmlProcessing = new AsyncSeriesWaterfallHook(['pluginArgs']);
compilation.hooks.htmlWebpackPluginAlterAssetTags = new AsyncSeriesWaterfallHook(['pluginArgs']);
compilation.hooks.htmlWebpackPluginAfterHtmlProcessing = new AsyncSeriesWaterfallHook(['pluginArgs']);
compilation.hooks.htmlWebpackPluginAfterEmit = new AsyncSeriesWaterfallHook(['pluginArgs']);
});
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
之前自己写的一个插件
class HtmlAfterWebpackPlugin {
apply(compiler) {
//每一次文件编译了告诉我
compiler.hooks.compilation.tap(pluginName, compilation => {
//然后htmlWebpackPluginAfterHtmlProcessing再进行hooks
compilation.hooks.htmlWebpackPluginAfterHtmlProcessing.tap(pluginName, htmlPluginData => {
let _html = htmlPluginData.html;
_html = _html.replace(/page:/g, '../../');
_html = _html.replace(/components:/g, '../../../components/');
const result = assetsHelp(htmlPluginData.assets);
_html = _html.replace('<!--injectcss-->', result.css.join(''));
_html = _html.replace('<!--injectjs-->', result.js.join(''));
htmlPluginData.html = _html
})
});
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17